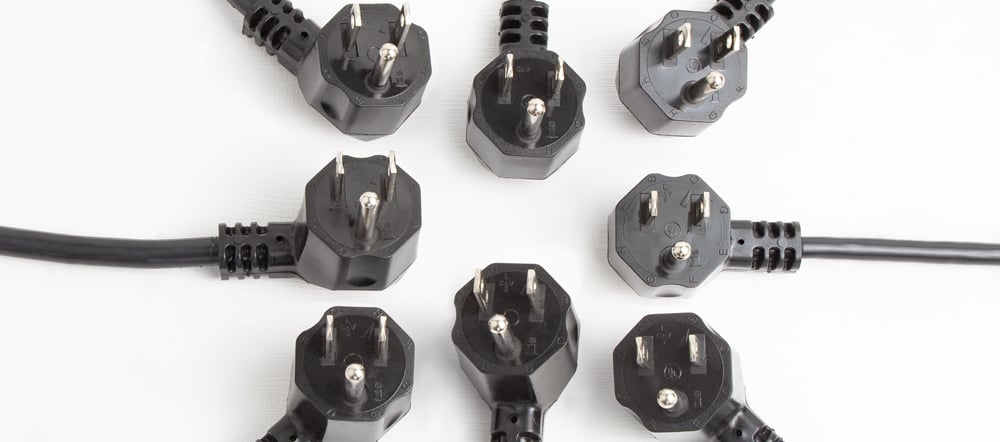
North American Angled NEMA 5-15 Plugs
Limited space between electrical equipment and the power connection can make the direction of the cord critical. An angled plug can minimize the space between connectors saving critical millimeters—having a huge impact. Different angles of plugs allow choices as to how a cord can be plugged into a power source. Angled plugs between connectors reduce the strain on both plug and cord.
 A |
 B |
 C |
 D |
 E |
 F |
 G |
 H |
 A |
 B |
 c |
 D |
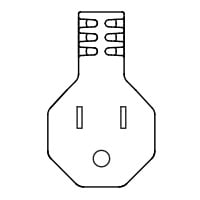 E |
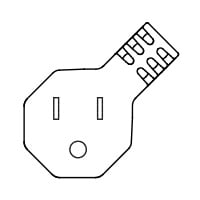 F |
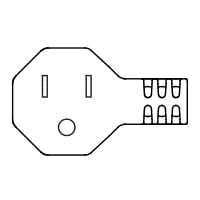 G |
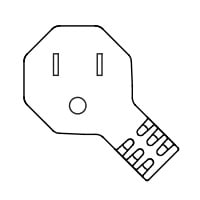 H |
The Eighth World Wonder?
Interpower offers eight different angles of the NEMA 5-15 plug. Though NEMA angled plugs provide critical plug and connector space for any industry, they are often “life savers” in hospitals and clinics where room space is often shared by patients and multiple machines.
They can also save critical IT connections from losing electrical continuity whether in a brick-and-mortar office, the “click-and-mortar” of cloud computing, or myriad servers residing in one location at a server farm—especially in power strips where strain reliefs and cable exits interfere with neighboring outlets. Shouldn’t a complex network of wires and cables have secure connections?
NEMA angled plugs are also great for commercial food service equipment where often food preparation space is cramped—large ovens, grills, and refrigeration units often block multiple outlets that often require an unconventional angled plug.
Testing
Just like the standard NEMA 5-15 plugs, the NEMA angled 5-15 plugs are subjected to the rigorous Abrupt Pull Test under UL 817, section 12.5. Clause 12.5.3.1 states: “Six representative assemblies consisting each of an attachment plug or current tap molded onto a flexible cord 0.3 m (12 in) in length are necessary for the test. Those having a ground pin in the up position, except for right-angle plugs, which shall be tested only in the cord down position.”
An angled plug may accommodate cramped space without staff having to move the equipment. A variety of plug angles allow a variety of choices on how a cord can be plugged into a power source.
Examples of where using an angled plug may be beneficial:
- Commercial food equipment on floors and counters often have minimal clearance for a plug.
- Equipment frequently pulled in and out for cleaning or relocation (reduces the opportunity to disengage the plug).
- Equipment located at an angle from the power source with a need for the cord set to plug in at a multidirectional angle.
- Applications where multiple devices are connected to a power strip. By choosing the correct angle, issues of plug strain reliefs and cable exits interfering with the next outlet in line can be avoided.
Additional Resources
Interpower can manufacture cord sets with angled plugs to meet specific requirements. Please contact Customer Service at info@interpower.com with specifications or for more information.


